IgA nephropathy is one of the most common kidney diseases. Unfortunately, it is a disease that has no cure and does not present symptoms in its initial stages either.
IgA nephropathy is a disease characterized by the accumulation of a protein (immunoglobulin A) in the kidneys. This causes inflammation and in the long term can severely affect kidney function.
IgA nephropathy is also known as “Berger’s disease” or “immunoglobulin A nephropathy.” The evolution of this pathology varies greatly from person to person. In some it disappears completely over time, while in others it causes end-stage renal failure.
There is currently no cure for IgA nephropathy. However, there are treatments to stop the progression of the disease. It can appear at any age, but it is more common in adolescence and in the third decade. Men are more likely to suffer from it.
Symptoms of IgA Nephropathy

IgA nephropathy is a disease with no cure; however, their progress may be halted.
IgA nephropathy is a slowly progressive disease. At the beginning there are no perceptible symptoms and, therefore, the pathology can be present for years or decades without being detected. The characteristic symptom is blood in the urine, but it is often so mild that it is difficult to notice.
Sometimes the disease is found in a routine urine test. This reveals the presence of proteins and red blood cells, which raises suspicion. It is also possible that after a cold or other infection, the urine turns pink or brown. That color reveals the presence of blood.
Other symptoms may be the following:
Urine that is dark or pinkish in color after vigorous exercise.
Foamy urine.
Pain in one or both sides of the back, in the lower part of the ribs.
Swelling in the hands and feet.
High blood pressure.
Large amount of albumin in the urine. It is only detected with a laboratory test.
If a person develops IgA nephropathy, usually 20 to 30 years after contracting it, other signs and symptoms appear, such as the following:
High blood pressure
Scarcity or absence of urination.
Inflammation.
Darkened and dry skin.
Generalized itching or numbness.
Cramps in the body.
Headache.
Nausea and vomiting
Weightloss.
Fatigue, drowsiness, and loss of appetite.
Sleeping problems
Difficulty concentrating.
What causes this kidney disease?
The function of the kidneys is to filter the blood; To do this, it sends the waste to the bladder to be expelled. The filtered blood, meanwhile, re-enters the bloodstream. On the other hand, immunoglobulin A (IgA) is a protein that helps protect the body from infections.
In the kidneys there are tiny filters called glomeruli. What happens in IgA nephropathy is that there is an accumulation of the IgA protein in such filters. Consequently, lumps form that damage the glomeruli. This is when the kidneys begin to fail and allow blood to pass into the urine.
For science it is not clear why this happens. However, it is believed that IgA nephropathy could be associated with the following factors:
Genes It is more common in certain ethnic groups and in some families.
Liver diseases. In particular, chronic hepatitis B or C infections, or cirrhosis.
Celiac disease Gluten seems to play a role in this disease.
Bacterial and HIV infections.
Risk factor’s
IgA nephropathy is a common kidney disease, but certain patterns have been found in those who have it. Based on this, it can be said that the risk factors for developing this pathology are the following:
Age. It can occur at any age, but it is more common during adolescence or between 30 and 40 years.
Sex. Men are three to six times more likely to develop IgA nephropathy.
Ethnic origin. This disease is more common among whites and Asians than blacks.
Family background. In some cases this pathology is hereditary, although not always.
Possible complications of IgA nephropathy
The most serious complication of this disease is acute or chronic kidney failure. It is estimated that one in 10 to 20 children with IgA nephropathy will develop kidney failure. The ratio in adults is one in four.
Other less serious and more frequent complications are the following:
High blood pressure. Kidney damage causes pressure to rise, and this, in turn, further deteriorates the kidneys.
High cholesterol. This increases the risk of heart problems.
Nephrotic syndrome. It includes manifestations such as high levels of protein in the urine and low levels in the blood, high cholesterol and lipids, and inflammation in the feet, abdomen and eyelids.
Henoch-Schönlein purpura.
How is it diagnosed?
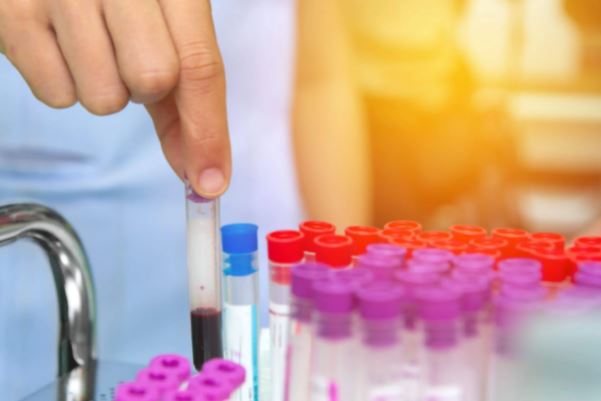

Faced with suspicion, the doctor will request a urine and blood test, and a biopsy to confirm the diagnosis.
It is very common that in the beginning there is only a suspicion that the disease is present. The doctor takes into account the family history and some symptoms such as pain or inflammation.
Also, the results of a blood test may suggest IgA nephropathy. Once the suspicion appears, what follows is to corroborate the diagnosis through clinical tests such as the following.
Urine analysis
Typically, a dipstick test is done for albumin and blood. The test involves taking a urine sample and putting a special paper called a “test strip” in it. If there is albumin or blood in the urine, the paper changes color.
A test for the relationship between albumin and creatinine may also be done. It consists of comparing the amount of both substances in the urine in a period of 24 hours. If there are more than 30 milligrams of albumin for every gram of creatinine, it is a sign of chronic kidney disease.
Blood test
The blood test is done to determine how much blood the kidneys filter per minute. That measurement is called eGFR. A result of 60 indicates that the function is performed normally. Below that figure suggests kidney disease. If it is less than 15, it is estimated that there is kidney failure.
Kidney biopsy
Kidney biopsy is the gold standard to determine if IgA nephropathy is present. While the other tests provide valuable clues, the diagnosis is only confirmed by biopsy. This consists of taking a part of tissue from the kidneys to analyze it under a microscope.
This test requires local anesthesia and light sedation. The results allow to verify if there are IgA deposits in the glomeruli, which are the small filters of the kidney. It also helps determine the extent of kidney damage and provides important clues for treatment.
Iothalamate debugging test
This test uses a contrast substance. This is a substance that allows you to better visualize how the kidneys filter waste. It is not a test that is practiced frequently.
What treatments are there?
IgA nephropathy has no cure, but treatment can help stop the disease from progressing. It also fulfills the goal of relieving symptoms and avoiding complications.
In general, treatment for IgA nephropathy is pharmacological and may include the following medications:
Drugs for high blood pressure.
Omega 3. These fatty acids are found in dietary supplements and may help reduce inflammation of the glomeruli.
Immunosuppressants. These drugs that suppress the immune response are sometimes indicated. They can cause serious side effects.
Statin therapy. They help lower cholesterol and protect against kidney damage.
Diuretics They are used to remove excess fluids from the blood.
There are serious conditions in which you must go to kidney dialysis. However, everything indicates that transplantation is better, since it has better results to prolong life and prevent the recurrence of the disease.
See your doctor if you have IgA nephropathy
There are no measures to prevent the development of IgA nephropathy. However, if any of the risk factors are present, it is best to watch for symptoms and consult your doctor if any abnormalities are detected.
A person with this pathology must have a regular medical follow-up. Keep an eye on your blood pressure values, reduce the amount of protein in your diet, and seek psychological support if required.